2 Atp Glycolysis
The hydroxyl groups allow for phosphorylation. Through this process the high energy intermediate molecules of ATP and NADH are synthesised.

Reactants And Products Of 10 Steps Of Glycolysis Pathway Embden Meyerhof Pathway Biology Glycolysis Pathways Biology Biochemistry Notes
The process also yields two molecules of NADH.

2 atp glycolysis. During this phosphorylation of glucose and its conversion to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate take place. A total of 2 ATP is derived in the process Glucose 2 NAD 2 ADP 2 Pi -- 2 Pyruvate 2 NADH 2 H 2 ATP 2 H2O. Thus the net energy yield in glycolysis is two molecules of ATP per molecule of glucose fermented.
Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that does not. Glycolysis consists of two distinct phases. In the first half of glycolysis two adenosine triphosphate ATP molecules are used in the phosphorylation of glucose which is then split into two three-carbon molecules as.
In the preparatory phase of glycolysis two molecules of ATP are invested and the hexose chain is cleaved into two triose phosphates. Glycolysis begins with glucose and breaks it down into two molecules of phosphoglyceraldehyde. The steps 1 2 3 4 and.
In glycolysis 4 molecules of ATP are produced when a glucose molecule is partially oxidised to form two molecules of pyruvate. During glycolysis glucose ultimately breaks down into pyruvate and energy. When glucose undergoes fermentation there is a net gain of 2 ATP molecules that occurs in the glycolysis process.
The specific form of glucose used in glycolysis is glucose 6-phosphate. Pyruvate molecules then proceed to the link reaction where acetyl-coA is produced. Glycolysis starts with glucose and ends with two pyruvate molecules a total of four ATP molecules and two molecules of NADH.
Glycolysis the first process in cell respiration produces four ATP but it uses two of the ATP molecules therefore producing a net two ATP molecules. Unique to tissues producing glucose ie. The first stage of cellular respiration is glycolysis.
Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes. Two ATP per glucose molecule are required to initiate the process then a total of four ATP are produced per molecule of glucose. Two ATP molecules were used in the first half of the pathway to prepare the six-carbon ring for cleavage so the cell has a net gain of two ATP molecules and two NADH molecules for its.
Glucose ATP -------- Glucose-6-phosphate ADP The two enzymes are reciprocally regulated or ATP would be lost without energy conservation. It is the same for both lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation. In the second part of glycolysis ATP and nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide NADH are produced Figure 416.
During Stages I and II of glycolysis two ATP molecules are consumed and four ATP molecules are synthesized. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate ATP and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NADH. How many ATP are formed in TCA cycle.
Glycolysis is the process by which one molecule of glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate two hydrogen ions and two molecules of water. If the cell cannot catabolize the pyruvate molecules further it will harvest only two ATP molecules from one molecule of glucose. During glycolysis one glucose molecule is split into two pyruvate molecules using 2 ATP while producing 4 ATP and 2 NADH molecules.
In glycolysis the net gain of ATP molecules is 2. In the first part of the glycolysis pathway energy is used to make adjustments so that the six-carbon sugar molecule can be split evenly into two three-carbon pyruvate molecules. This process utilizes two molecules of ATP for energy.
Glucose-6-phosphate produced from the gluconeogenic pathway is transported to the ER for dephosphorylation. In the second part of glycolysis ATP and nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide NADH are produced Figure 442. Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 into pyruvic acid CH 3 COCOOH.
It does not require oxygen. However maximal ATP yield from oxidation of glucose is 36 to 38 ATP.

Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Math Methods Learning Math
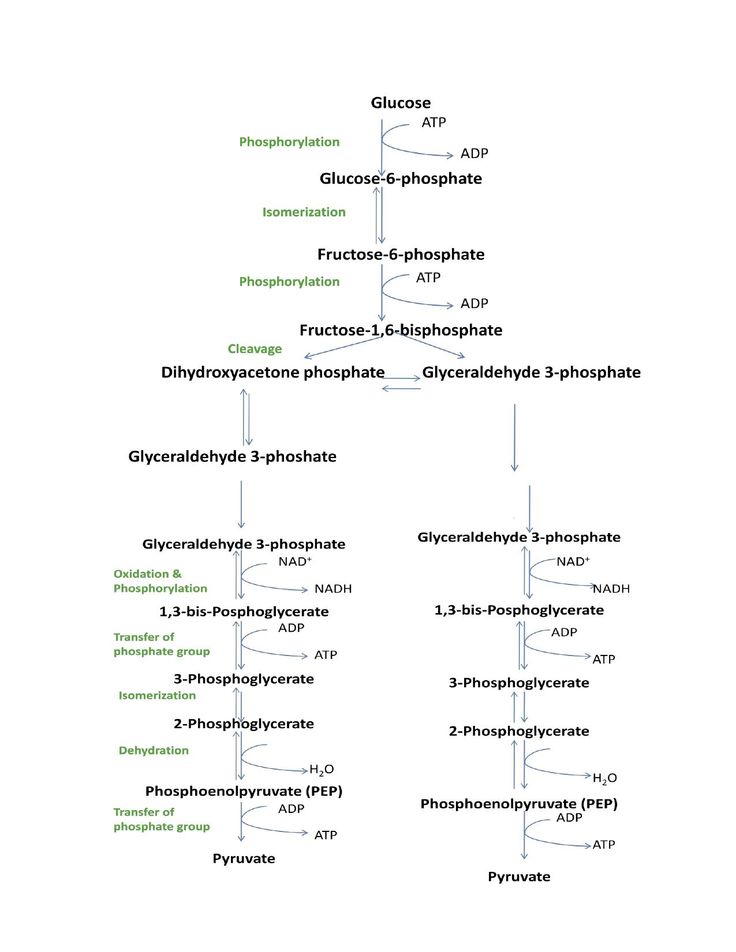
Respiration L Production Of Atp Science Biology Study Smarter Biochemistry

Note If Glycogen Enters In Glycolysis Net Gain Of Atp 3 Biochemistry Molecules Chart

Tj Glycolysis From Glycose An Older Term For Glucose Lysis Degradation Is The Metabolic Pathway That Science Cells Biochemistry Medical School Studying

Cellular Respiration Diagrams Medical Student Study Biochemistry Med School Study

Glycolysis For Dummies Biology Notes Cellular Respiration Biochemistry

10 Steps Of Glycolysis Biology Classroom Photosynthesis Worksheet Biochemistry

Biology Flow Chart For Cellular Respiration Studypk Teaching Biology Biology Classroom Science Biology


Posting Komentar untuk "2 Atp Glycolysis"